ELVA’s ARTICLE:
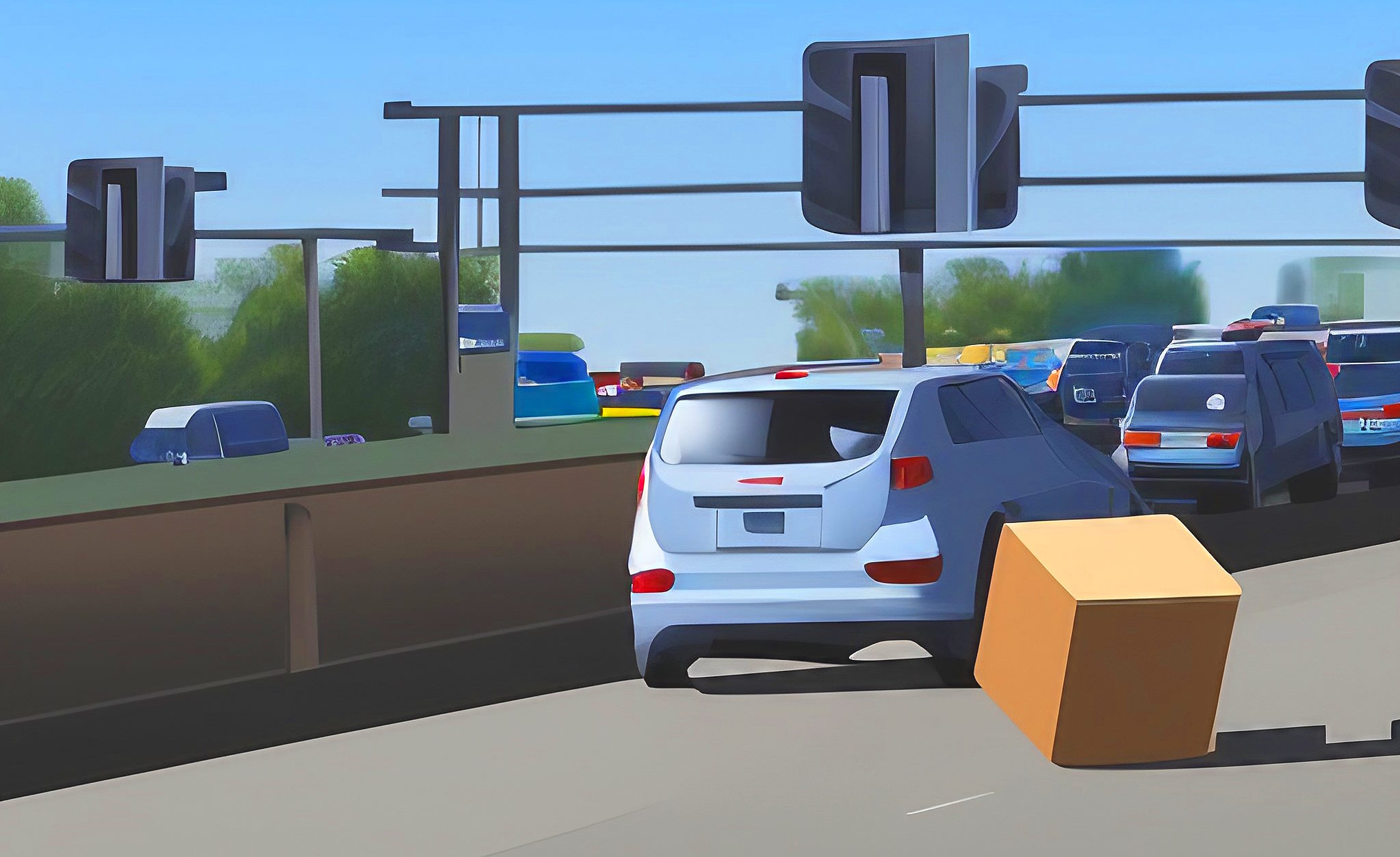
ELVA-1 road monitoring radar detects min target on the road surface as box of 30x30x30 cm
ELVA’s E-band mm-wave SDM360-76RM Road Monitoring Radar Sensor is well-suited for road monitoring in the United States and Europe due to several key advantages it offers over other brands.
Each year, thousands of accidents on highways are caused by fallen loads from vehicles. Even a small item like a one-foot-long box or a piece of furniture falling off a car can cause a major accident if other drivers on the road have to maneuver sharply to avoid it.
This sudden maneuvering can lead to collisions, loss of control, and even vehicles driving off into ditches or down embankments. However, there is a solution to this problem: radar monitoring of the surface of highways. In this article, we will explore the importance of radar monitoring in preventing accidents caused by fallen loads and other causes of accidents, and how this technology can help ensure safer roads for all drivers.
Why it is especially important to monitor highways for fallen cargo, stalled cars, walking people and animals? Unsuspecting drivers do not have time to stop in front of the scene of the accident. On U.S. and European highways, this is a serious problem, since mass accidents are too common.
Let us be honest, traffic radars themselves are not a revolutionary new technology. For example, those operating in the 5 to 24 GHz band have long been installed for traffic counting. However, it is the E-band radars that offer new opportunities, as they can detect even small objects on the road and animals the size of dogs and larger.
Importantly, mm-wave E-band radars can detect not just small objects on the road, but such radio-transparent things as empty cardboard boxes that old-fashioned centimeter-wave radars are unable to detect. Of course, an empty cardboard box is not dangerous for cars, but it is the driver’s maneuver that is dangerous. Because such a driver dodges an obstacle on the road unexpectedly for other road users.
As a minimum target on the surface of the road can be called an empty box measuring 30x30x30 cm, because this is the size of the obstacle, which is already starting to scare drivers and make them maneuver.
Why low-frequency radars cannot detect small objects on the road surface
Low operating frequency radars, which typically work within the 5 to 24 GHz range, are generally less suitable for detecting small objects like dropped cardboard boxes compared to high-frequency radars such as E-band radars, which operate at 71 to 95 GHz. The reason for this is that the wavelength of the radar signal is inversely proportional to its frequency. Higher frequency signals have shorter wavelengths, allowing them to detect smaller objects more accurately. Also radio transparency of a target plays its role in successful detection.
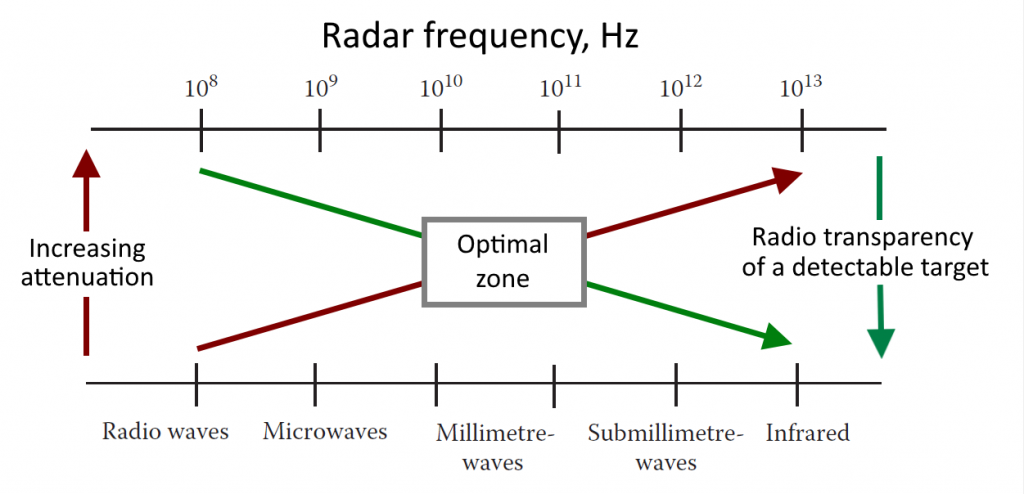
Radio transparency of a detectable target depends on the radar frequency. Millimeter waves are the optimal zone when the radio transparency of the detected target is reduced (therefore, the target becomes visible to the radar), but the attenuation in the atmosphere and precipitation is not yet so great as to impact to radar performance.
Radio transparency of a target refers to the ability of a material or object to allow radar waves to pass through it without significant reflection. In other words, radar-transparent materials do not reflect radar signals, allowing them to pass through with minimal distortion. Cardboard boxes are an example of radar-transparent targets because they are made of lightweight, low-density material.
In general, materials that are radar-transparent are those that have low dielectric constants and low electrical conductivity. Conversely, materials that are highly reflective or absorptive of radar signals, such as metals or water, are considered radar-opaque or radar-absorbing.
The radar transparency or opacity of a material can play an important role in the design and effectiveness of radar systems, particularly in applications such as detecting small objects like cardboard boxes on highways.
However, it’s important to note that different radar systems are designed for different purposes and have varying capabilities. While low-frequency radars may not be ideal for detecting small objects like cardboard boxes, they may perform better for other applications, such as monitoring larger objects like vehicles or aircraft. Ultimately, the choice of radar system will depend on the specific requirements and objectives of the application.
The mission of E-band road monitoring radars is to prevent mass accidents and provide road operators with early warning data about potential hazards on the road. This allows road operators to act quickly, informing drivers in advance and thus effectively preventing accidents to ensure the safety of road users.
How to choose the best radar sensor for road monitoring
When a road operator is selecting a monitoring radar system to detect road accidents, debris on the road surface, stopped cars, people and animals on the highway in any weather, there are several important characteristics to consider.
Here are 9 recommendations for such customers to keep in mind:
- Frequency band. Make sure the radar system has an optimally long range, such as 200-250 meters, to provide ability to observe a sufficient part of the road. A very long range of the monitoring radar, e.g., 1 km, will result in the road not being viewable due to many cars obscuring the radar picture of the road surface within the zone.
- Range: Make sure the radar system has an optimally long range, such as 200-250 meters, to provide ability to observe a sufficient part of the road. A very long range of the monitoring radar, e.g., 1 km, will result in the road not being viewable due to many cars obscuring the radar picture of the road surface within the zone.
- Doubled covered area. Radar has an all-around view, and under certain conditions, it can be set so that the range is provided in two directions of the road, with the total length of the monitored zone will be 400-500 meters (200-250 meters in one direction and 200-250 meters in the other direction). Under certain conditions means using on the road curves, roundabouts of the road, or radar stand a little to the side on straight stretches of highway so there is no dead spot under it.
- Project budget. 200-250 m is optimal for radar range in terms of cost and accuracy of obstacle detection. For example, if radars are installed much more frequently, like every 50 m, they have a better chance of detecting a fallen load, a person or animal, a broken-down car, or other targets. But if radars are placed frequently, the cost of the project will increase significantly. On the contrary, if you install radars covering an area of 1 km the project will be cheap, but the quality of monitoring the road surface will be very reduced. That is why 200-250 m is the optimum range.
- Detection capabilities: Ensure the radar system is able to detect debris of a noticeable size, including obstacles which are radio-transparent for other types of radars. This will help operators respond quickly and effectively in case of an emergency.
- Weather resistance: Look for a radar system that is designed to operate in all weather conditions, including snow, sleet, and fog. This will ensure that the system remains reliable and accurate even in challenging weather conditions.
- Interference resistance: Choose a radar system that is designed to resist interference from other sources such as other radar systems because of narrow beam in a high-frequency band. This will help to ensure that the system provides accurate and reliable data even in areas with high levels of electromagnetic interference.
- Ease of use: Select radar units that are easy to install and operate, with a digital interface. This will help ensure that the operator’s technical team can effectively manage the radar system.
- Light licensing. Depending on the country, there are different rules from local regulators about the use of radars for highway monitoring. For example, in the USA, the FCC permits unlicensed use in the 70-71 GHz range for any radionavigation services intended for safety (FCC’s Federal Radar Spectrum Requirements). In Europe, mm-wave radars are permitted as radiodetermination equipment for ground based vehicular applications within the frequency range 77 GHz to 81 GHz (ETSI TR 103 593).
By considering these characteristics when selecting a road monitoring radar system, customers can ensure that they choose a system that is reliable, accurate, and effective in detecting road accidents, debris and stopped cars on the highway in any weather. This will help to keep road users safe and minimize the risk of accidents and other emergencies.
Introducing SDM360-76RM Radar Sensor for Road Monitoring

In the previous sections we told you about radar road monitoring system in general terms. Now it’s time to present SDM360-76RM Road Monitoring Radar Sensor which is designed to detect stopped vehicles, debris, people and animals on highways in real-time, allowing operators to respond quickly and effectively to keep road users safe.
The SDM360-76RM sensor uses millimeter-wave radar technology within E-band spectrum to detect objects in low visibility conditions. It can detect vehicles and debris at distances of up to 200 meters in both directions of the road (400 m length in total) with an accuracy of 15 cm, providing both a considerable viewing distance and saving the budget of road operators.
The term millimeter-wave radar sensor is used and it differs from just a radar. To explain, a radar is a fully functional device which has its own screen and device controls for human personnel to assess the situation in the monitored area. he radar sensor is a detecting unit only and it just transmits a digital signal to the road operator’s control room, where it is further algorithmically processed in the computer system.
In situations where the SDM360-76RM Traffic Monitoring Radar Sensor detects an obstruction to normal traffic, it sends an alarm to the traffic control room and they can dispatch emergency services or take other necessary actions. Without the SDM360-76RM Traffic Monitoring Radar Sensor, road obstacles might go unnoticed and become a danger to drivers.
The SDM360-76RM Road Monitoring Radar Sensor can also help prevent accidents caused by wrong-way drivers. In many cases, wrong-way driving occurs because a driver is confused or disoriented, perhaps due to poor visibility or a lack of clear signage. The radar sensor can detect these drivers and alert road service or police so that they can take action to stop them before they cause an accident.
It should mention the primacy of the SDM360-76RM radar sensor as the most effective device detecting debris on the road surface due to the operation at frequencies above 70 GHz. During the SDM360-76RM tests, a 30x30x30 cm (1 foot box size) an empty cardboard box was easily detected within 200 m distance.
Remarkably, the 76 GHz radar was able to detect an empty cardboard box, as this is a very difficult object to detect for other types of radar.
Low-frequency of traffic radars, such as those operating at 5 GHz or 24 GHz, are not capable of detecting debris. Automotive radars installed on vehicles are also unable to detect debris because they are designed to respond to other moving vehicles.
The case of a fallen-out on the road is the most important application of E-band radar, because for radars in other bands such a small road debris target may be undetectable due to the low radar cross section parameter (RCS) value.
SDM360-76RM Road Monitoring Radar Sensor for Safety in Tunnels
Radar sensor for road monitoring is especially important for surveillance in tunnels during fires caused by an accident, when video cameras do not work due to smoke. In the event of a tunnel fire, smoke can quickly fill the space, making it difficult or impossible for video cameras to get a clear image. This can make it difficult for emergency services to locate vehicles, and to find and rescue people in the tunnel. E-band radar sensor provides reliable object detection even in poor visibility conditions.

Road monitoring radar of E-band, however, is not affected by smoke and can provide reliable data on the location of objects in the tunnel. This information can be crucial for emergency services, allowing them to quickly and efficiently locate vehicles and people in the tunnel.
In addition, E-band road monitoring radar can be used to provide real-time data on traffic flow and tunnel conditions, which can be used to help emergency responders respond more effectively and safely to emergencies or traffic jams. This can help limit the admission of vehicles into the tunnel in time and minimize the risk of accidents and injuries during tunnel emergency response operations.
E-band Spectrum Advantages for Radar-Based Road Monitoring
The E-band mm-wave spectrum used by ELVA-1 SDM360-76RM Road Monitoring Radar Sensor is particularly well-suited for road monitoring in the United States and Europe due to several key advantages it offers over other bands.
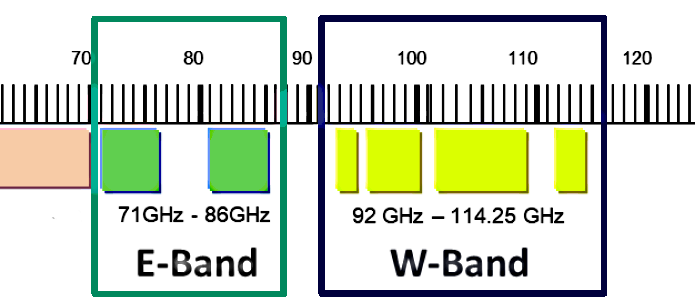
The SDM360-76RM traffic monitoring radar can be manufactured to operate in the 70-71 GHz, or 76-77 GHz, or also 80-81 GHz or 94-95 GHz frequency bands, occupying the 1 GHz spectrum bandwidth, to meet the regulatory requirements of different countries. In other words, the radar sensor can be manufactured for a specific band that is ordered by the customer.
It should be again clarified that the width of the occupied frequency bandwidth for the radar sensor is 1 GHz. Therefore, according to the customer’s specs and depending on the restrictions of the local legislation it is possible to manufacture the radar sensor in any of the following sub-bands:
- 70-71 GHz,
- 71-81 GHz (mostly in Europe),
- 94-95 GHz,
- Above 95 GHz (here FCC allocates 95 to 100 GHz band for radionavigation safety services).
The radionavigation service is defined as “radiodetermination used for the purpose of navigation, including obstruction warning.” The radionavigation service is unique in that it is referred to as a safety service—any radiocommunication service that is used permanently or temporarily in the safeguarding of human life and property.
Source: FCC Federal Radar Spectrum Requirements.
The advantages of the E-band for road monitoring radars are as follows:
First, the E-band spectrum is a high-frequency one, which allows for increased resolution and accuracy in detecting objects on the road. This is especially important in low visibility conditions such as snow, sleet, and fog, which can make it difficult for other radar systems to detect objects.
Second, the advantage of the E-band band is that it is a relatively new and emerging technology. This means that it is likely to see continued improvements and advancements in the coming years, which will further enhance its capabilities and accuracy.
Overall, the mm-wave band used by the SDM360-76RM Road Monitoring Radar Sensor is an excellent choice for road monitoring in the United States, Canada and European countries due to its high resolution, low interference, and potential for continued improvements in the future. By using this advanced technology, road operators can help to ensure that drivers remain safe and accidents are minimized, even in challenging winter weather conditions.

If you’re an operator planning to install road monitoring system on American or European highways to use especially during harsh weather conditions, be sure to keep an eye out for the SDM360-76RM Road Monitoring Radar Sensor and then take comfort in knowing that your roads are being protected by the latest in advanced safety technology. The radar sensor uses 76 ±0.5 GHz in its basic version and can be also manufactured in customized frequency within E-band spectrum.
